Programming Tutorials
Code Logic Input Output Data Storage Smart Technology

Binary
Binary code is the simple language that computers use to compute. Think of binary as a bunch of on/off switches where 0 is False, 1 is True.

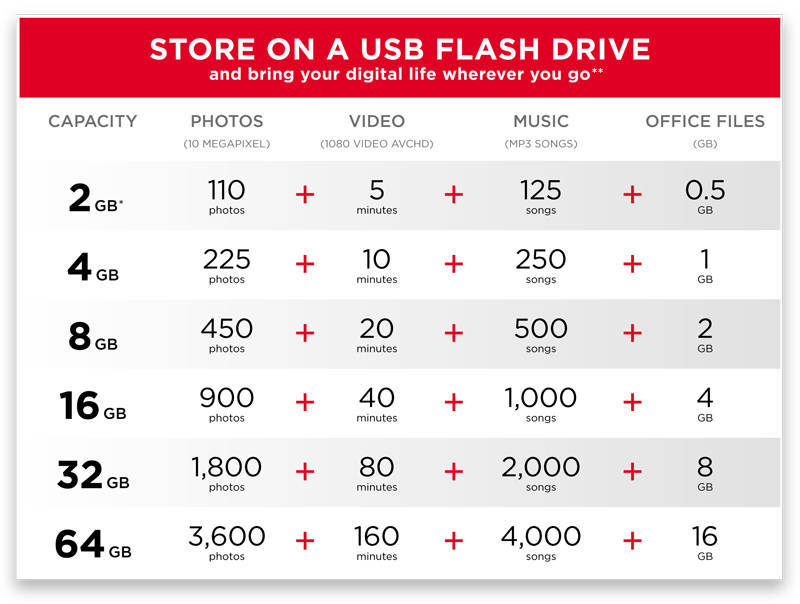
Bits and Bytes
Bits are tiny capsules of information. Each bit represents either a 0 or a 1. There are 8 Bits in 1 Byte, and 1,024 Bytes in a Kilobyte, 1,024 KB in 1 Megabyte, 1,024 MB in 1 Gigabyte, and 1,024 GB in 1 Terabyte.


ASCII
ASCII stands for American Standard Code for Information Interchange. ASCII is used to convert the characters on a keyboard into numerical data values that the computer can read. Without ASCII, people would have to try to decode a bunch of numbers on screen, but this system performs the conversions automatically.


Matrices
A matrix is an array of data values, sort of like a spreadsheet but without the border lines. Computers store trillions of data values, so theoretically the visualization of a matrix would be depicted as an endless string of numbers arranged in columns. The more accurate representation would be a layered 3-dimensional grid to indicate separate container folders. Sadly, this is all theoretical, since matrices don't really look quite as cool as they do in the movies.


Data Encryption
Data encryption is used to ensure information stored on a computer is unreadable to outside parties. The information is safeguarded by a cipher, which consists of a long string of computer jibberish that would take a human millions of years to try and guess the correct password. Only certain computer devices can interpret the cipher key to translate encrypted data into plaintext people can read.
Unfortunately, skilled hackers and shady government organizations like the NSA can sometimes circumvent ciphers and firewalls to steal information or tap your internet browsing history. Hackers can remotely access any computers and phones that are not protected by a secure network server. To truly be safe, it's best to keep important records on a flashdrive in a hermetically sealed underground vault protected by lava moats and guard dragons. Also, make sure your administrator password isn't 1234, your pet's name, or your birthday date.
TED Talks: Hackers- The Internet's Immune System | Keren Elazari
TEDx Midwest: Top hacker shows us how it's done | Pablos Holman
TEDx Reykjavík: Why I teach people how to hack | Ýmir Vigfússon
SearchSecurity: Encryption
Popular Mechanics: It's Crazy How Fast a Computer Can Smash Through Your Puny Password


Analog vs. Digital
Analog technology can be used to store information in a solid state. Film, VCRs, Floppy disks, CDs, Records, Clocks, and old NES cartridges can be considered analog technology. Analog has fallen out of favor since digital storage can store far more memory in less space. Digital information can also be backed up on cloud storage, which is useful if hardware gets damaged or destroyed. Analog technology has one advantage in that it cannot be hacked remotely, because it doesn't connect to a wireless network.


RAM vs. ROM
Random Access Memory is impermanent memory storage on a computer that gets deleted when the computer is shut down. Read-Only Memory is more permanent and cannot be altered directly, it can only be read. Computers operate using ROM.

Circuitry
Refined silicon is used in electronic manufacturing for its high semiconductor properties. Only a small amount of industry grade silicon is needed to create an integrated circuit wafer. These wafers will be built into the motherboard of a computer or electronic device.
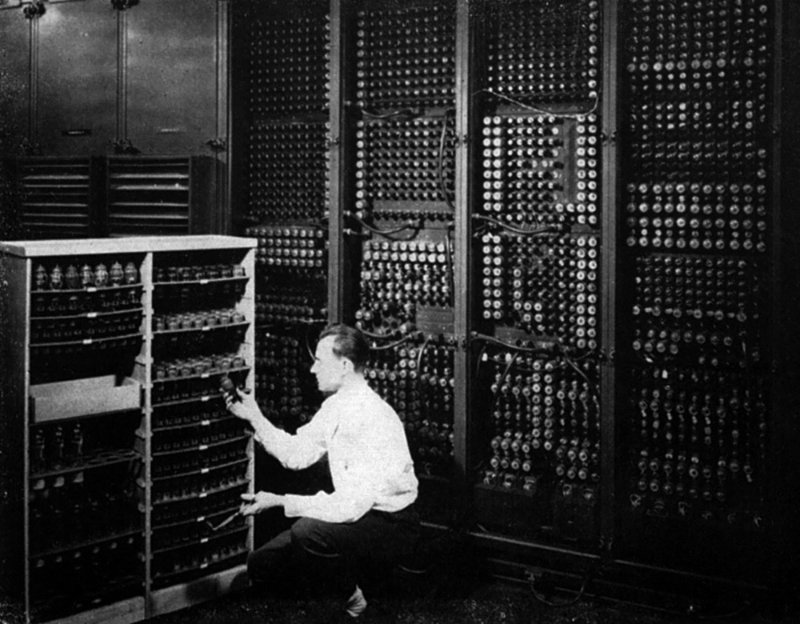


Computers
Computers have developed in three major steps. The first generation of room-sized computers used vacuum tubes, which were bulky and fairly unreliable. The tubes constantly had to be replaced by hand when they stopped working. These computers could only perform math calculations and all input and output was completely analog. There wasn't a mouse, keyboard, or display monitor. Information was stored by punching binary holes onto paper strips that could be fed into the machine.
Transistor computers were developed in the 1950's and lasted until the 1960's. They used magnetic memory cores, which are a non-volatile means of safely storing memory. Magnetic cores were eclipsed when semiconductors were invented, which reduced manufcturing costs and allowed increased memory storage. Modern Third Generation computers use integrated circuits, silicon wafers, and other processors and drivers to perform complex tasks that early computer scientists could only dream of.
Gameranx: Evolution Of PC Gaming Hardware
Gameranx: How Do GRAPHICS CARDS Work?


Currents
Electrical currents are used to transfer energy and signals. Direct current is generally used for power transfer cables. Alternating current forms a sine wave that can carry encapsulated data, such as the type used to stream video or audio. A transmitter and receiver are required to convert signals into a form people can use.

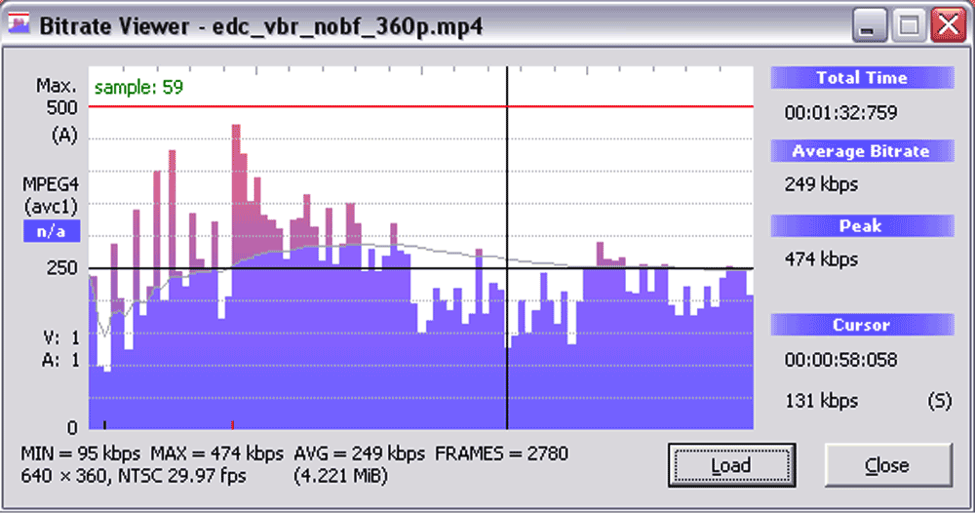
Bit Rate
When large files are transferred or read, the computer cannot download the entire file at once. Instead, it must gradually send over parcels of data bits. The amount of data that can be transferred per iteration is the bit rate.
Computers sample at a set rate each time they download, which alters the original source very slightly. This means that re-downloading the same file multiple times will eventually cause degradation of the file quality.
Video Data Degradation caused by resampling 1,000 times
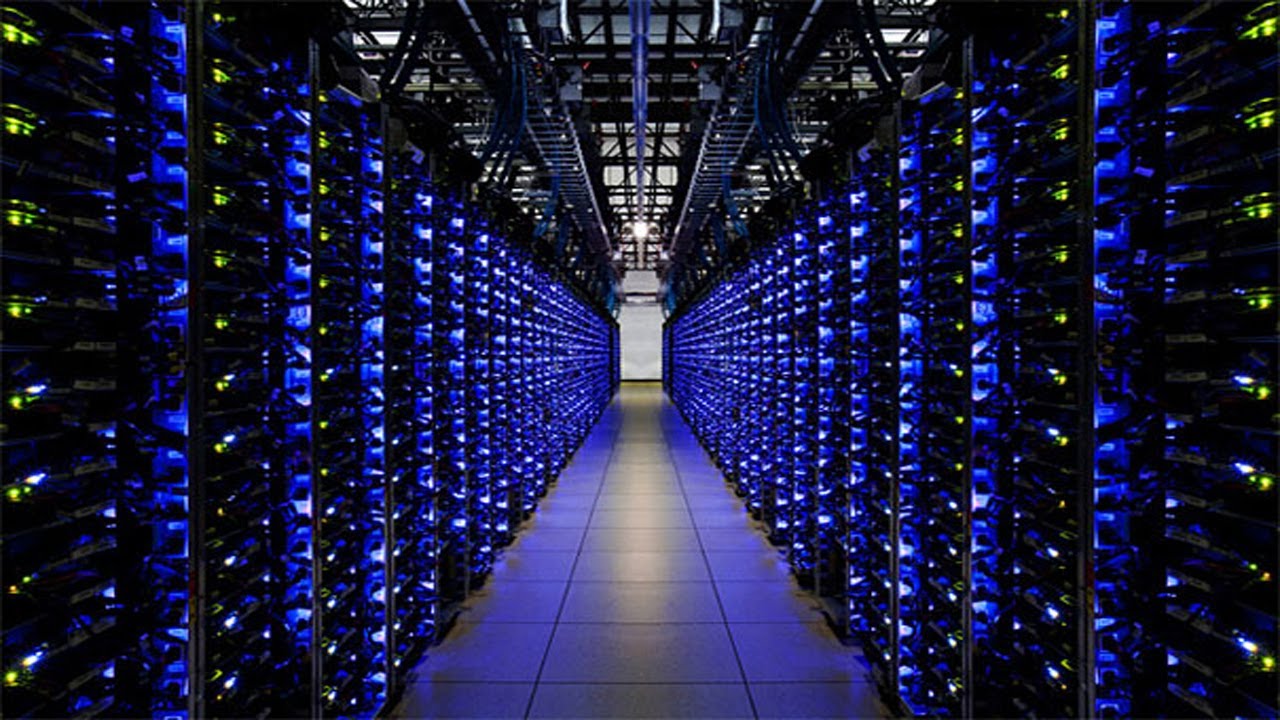


Modems, Servers, and Wireless Networks
Servers are large data storage centers that generally comprise of several hundred or several thousand computer hard drives stacked together. These centers can be linked together to form giant data banks, also referred to as supercomputers. Server rooms generate a lot of heat and require complex cooling systems and temperature controlled rooms to prevent hardware failure.
Servers transmit information to modems, which then send signals out to the routers used in homes, workplaces, or personal devices. This forms the rudimentary basis for how the internet works by connecting data stored on computers across the world.
Interconnected technology makes it possible to store inconceivable amounts of information in powerful supercomputers, neural information networks, and the mobile cloud. Keeping everyone connected means that big data, network traffic, and service providers will continue to be extremely relevant in the future.
Inside a Google data center
Nat & Lo: What Actually Happens When You Watch A YouTube Video?
The Atlantic: Net Neutrality: A Guide to (and History of) a Contested Idea


Algorithms
Algorithms are sets of programmed mathematical formulas and instructions. A function by itself can only do one specific task, but put a bunch of them together, and you can create a very complex system. Algorithms generally are set up to be performed in a specific order to cycle through multiple variations and possible solutions. A computer can perform these calculations in split seconds.
Lego Cubestormer 3


Queries
A query is an algorithm that will take an input and return results from a database based on a set of parameters. Google's search engine operates on a very advanced set of query algorithms.
Google: How Search Works

Machine Learning
Computer science has gotten significantly more complex over the years. The first vacuum tube powered computers filled entire rooms but could only perform the calculations of an average calculator. The systems used today can automatically gather feedback information that can be used to autocorrect, adjust performance, and improve results.
Artificial Intelligence programming is the most complex form of theoretical cybernetic system. An A.I. operates like a vast neural network which can store and access vast quantities of information. So far programmers have made breakthroughs in creating machines that can outperform humans in very selective logic exercises and memory capacity, but they have yet to create a system that can truly adapt or think independently like a human brain.
These proto A.I. also still fill up entire rooms with stacks of computers. Until quantum computing is mastered, it's unlikely an A.I. brain will fit into a humanoid mechanical body, so that's one major obstacle machines will have to overcome if they ever gain sentience and decide to enslave humanity. A.I. remains a theory until then.
Mashable: 1996-1997 The Kasparov-Deep Blue chess matches
NY Times: Google’s Computer Program Beats Lee Se-dol in Go Tournament
IBM Watson: The Science Behind an Answer
BBC: Computer AI passes Turing test in 'world first'
Bloomberg: Apple’s Deep Learning Curve- The company’s secrecy is hurting its AI software development


Programming Languages
Even though computers can only read binary, there are many different programming languages and software engines. These languages use different variations of syntaxes and are sometimes only compatible with certain types of machines or software.
A compiler is a special type of program used to decipher a programming language into fundamental machine code binary. A decompiler switches the machine code back into an output. There's a bunch of other complex processes, translations, and reformatting that occurs in-between these steps, but all you really need to know is that modern compilers are a lot more flexible at interpreting different code types than computers made over 30 years ago. This means that programmers can start out learning just about any language and build up knowledge from there.
Code.org: What Most Schools Don't Teach
Codementor: What Programming Language Should a Beginner Learn?
The Wall Street Journal: Why I’m Not Looking to Hire Computer-Science Majors (competition in the real world)


Terminology
Programmers have developed an extremely complex lexicon of software terms that they can use to communicate with other programmers across the world despite using different code platforms. This is due to the established standards and similarities between code languages. To regular people though, programming terms sound like complete jibberish.
Trying to wrap your head around what modules, subroutines, instances, shell scripting, and various acronyms mean is initially quite tough, especially for visual learners. It just takes practice. The nice thing about learning to code is that you'll be able to exchange hilarious inside jokes in conversation with your programmer friends while everybody else just looks confused.
Glossary of Computer Programming Terms

Logic and Syntax
Computer logic functions on the principle of binary absolutes. If code is not phrased in the proper syntax, the computer won't be able to translate the information, and an error will occur. You will be reminded of this simple fact quite frequently when your code doesn't do what you wanted it to. It's just a hard lesson all programmers must go through.


Debugging Code
When improper syntax doesn't crash the system, freaky things can sometimes happen instead. This is usually attributed to a missing or deleted closing div, or else a slightly mispelled word. Even capitalization can cause problems. Sometimes one line of code is overridden by another block of code with conflicting influence. When code misbehaves, the only thing to do is just go back through the thousand lines of code for the fortieth time and try not to break down in tears. Methodically deleting swathes of code and refreshing is an unorthodox but generally effective way to try and isolate the source of errors.
Medium.com: Ken Mazaika- 29 behaviors that will make you an unstoppable programmer


Standard Code Annotation
It is a good practice to make a habit of always naming files and annotating code using standard conventions. The reason for this is that when something stops working properly or needs to be changed, it makes it much easier for anyone to go in and pick out the correct block of code. You don't want to waste hours going through someone else's 30,000 lines of Java jibberish trying to figure out what controls what.
Free Code Camp: Coding Explained in 25 Profound Comics


Efficiency
In programming, you generally want to be as efficient as possible with code. If something can be done with one line of code instead of twenty, it is preferable to use the one line of code. The further you delve into programming, the more advanced ways you will find to rearrange bundles of code into neater systems that take up less memory and run far more efficiently.
Your first coding project isn't going to be pretty or compact. However, a good programmer always seeks to learn new techniques and tries to improve the underlying infrastructure of their code.
Garry Houser
Yosefk: Redundancy vs. Dependencies: which is worse?

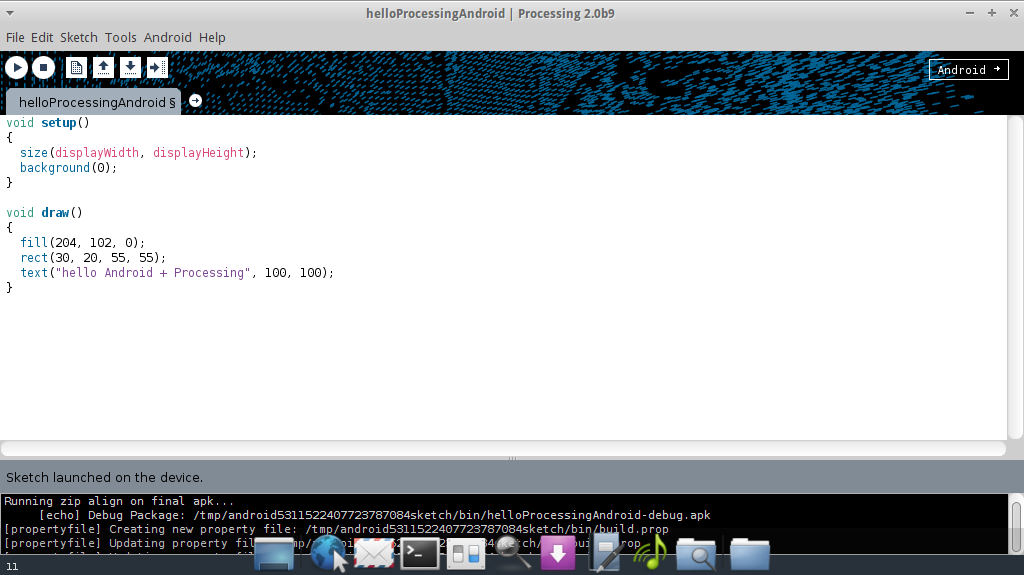
Setup
Processing has three main steps: declaration, initialization, and draw. Integer and char values are assigned by declaring values, usually placed before the initialization part. Void setup() {} is a default class used to initialize values and instructions. Any code that appears between the curly brackets will act as instructions. Void draw() {} represents the active elements that will be displayed in the view window when the code is running.
Processing.org: Objects

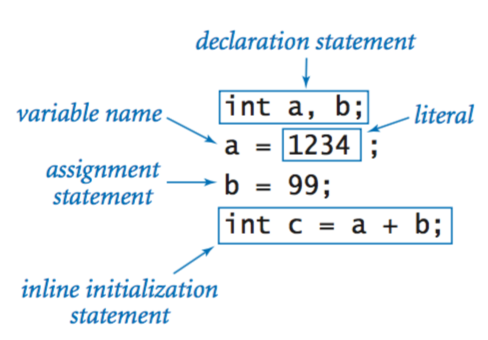
Declaration Statements and Assigned Values
This involves some basic algebra, assigning values to integers. The programmer has to put the declaration statement in the correct syntax within the code. Once a variable is declared once, it can be used multiple times or be assigned to functions and other variables.

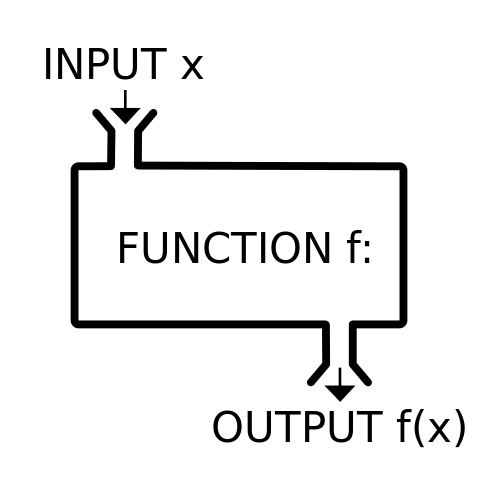
Functions
Functions are math formulas. For Loops, While Loops, and Else Statements are the type you'll probably be dealing the most with. For loops cycle through a set number of values and applies a formula eac time until the parameters of the statement are met. Else statements will switch to another formula if the parameters of another formula are untrue.

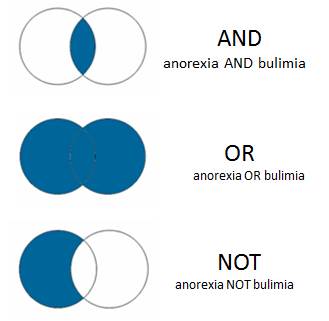
Boolean Operators
If, And, and Not are logic statements used to join functions. Multiple functions can be strung together using these operators.

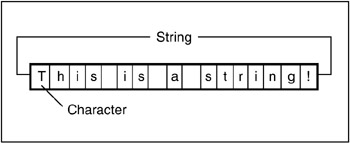
String
A string is a set of characters. It can be broken down into substrings. length() will return the number of characters in the string. print can be invoked to display characters on screen.

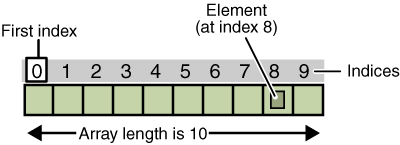
Arrays
Arrays are used to store a large number of values of similar type. They can be used in conjunction with For loops to apply a function to multiple objects at the same time.
Jose Sanchez: Processing Arrays


Probability
A seed value is used to initiate a randomization generator that will return a value from a range of values. This process is tecnically pseudorandom and based on probability rather than randomness, but that's a subject for lengthy discussion with your statistics professor. The random function can be used with any kind of defined value, including integers, colors, coordinate points, shapes, etc. The seed will determine how many things are returned for each function.
IFA.tv: Probability Machine/Galton Board, Randomness and Fair Price Simulator

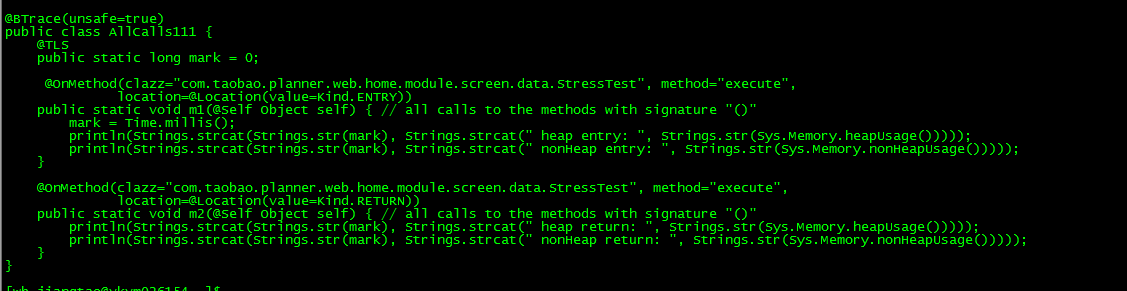
Calling a Function
Object-Oriented programs allow the programmer to reuse predefined code by referring it. This saves writing a bunch of lines of code over and over. If you ever look at a video game's source code and there seems to be far less lines of code than expected, it is because all the data is being called in from other source folders.

Classes
A Class is a grouping of functions that can be set up as an object instance. A class is set up using this format: class Nameofclass{function/s go here}. Every time the class is invoked, it will generate whatever the functions are set up to create. This can be used to create different types of sprites.
Coding For Art: Objects and Classes

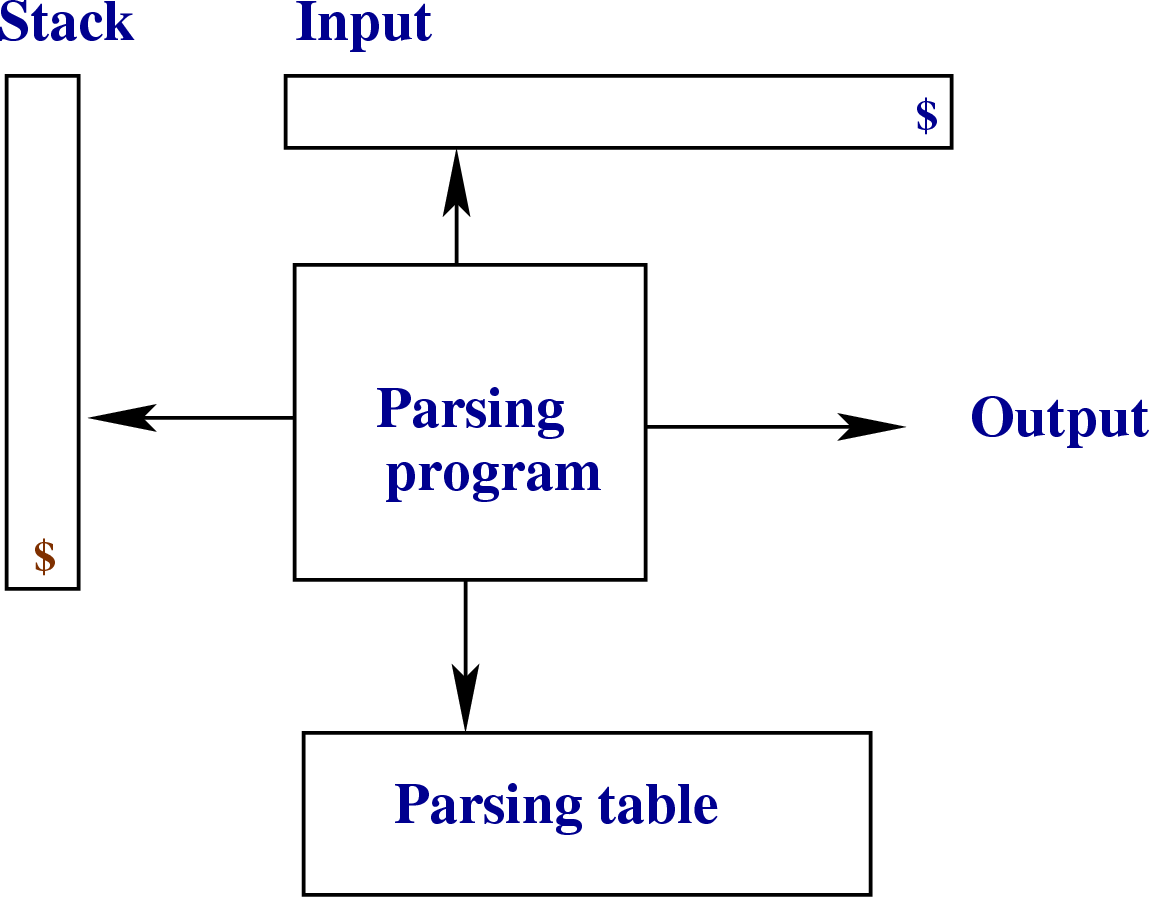
Parsing
Parsing is a logic process used to take unorganized characters and convert them into a syntax tree. Basically when a person inputs a sentence into a computer, the computer wouldn't know how to display those words in order to make any sense without parsing sorting out where letters and punctuation should go. Top-down and Bottom-up are the two alternate parsing methods.
Parsing posed a big headache for the first programmers, but these days parsing is already built into most compilers, so programmers don't have to worry about it too much unless you plan on building your own engine or program.

Recursion
To understand recursion, you must first understand recursion. To understand recursion, you must first understand recursion. To understand recursion, you must first understand recursion. To understand recursion, you must first understand recursion. To understand recursion, you must first understand recursion. To understand recursion, you must first understand recursion. To understand recursion, you must first understand recursion. To understand recursion, you must first understand recursion....
Recursion is a procedure that is defined in it's own terms, creating a redundancy error that spirals into an infinite chain of itself. Recursion differs from a loop, which is a procedure set to cycle a set number of times. A recursion can be thought of as more of a paradox, rhetorical question, or logical fallacy where instead of giving the function a defined value to repeat, you tell it to repeat the same function. The computer doesn't know what to do with this open-ended statement that doesn't have parameters or a returnable answer, so it freaks out and just goes bananas, spawning infinite instances until the program crashes or gets turned off.


Self-Similarity
Fractals and Sierpinski's Triangle are examples of self-similarity, though they can also be generated using recursion. Self-similarity describes something that has components that are exactly similar or partially similar to itself, but at a different scale. Fractal patterns are weird since they can also be found in nature. Mathematicians and scientists find this particularly fascinating, and it's not hard to see why.
TEDxGreensFarmsAcademy: The surprising beauty of mathematics | Jonathan Matte

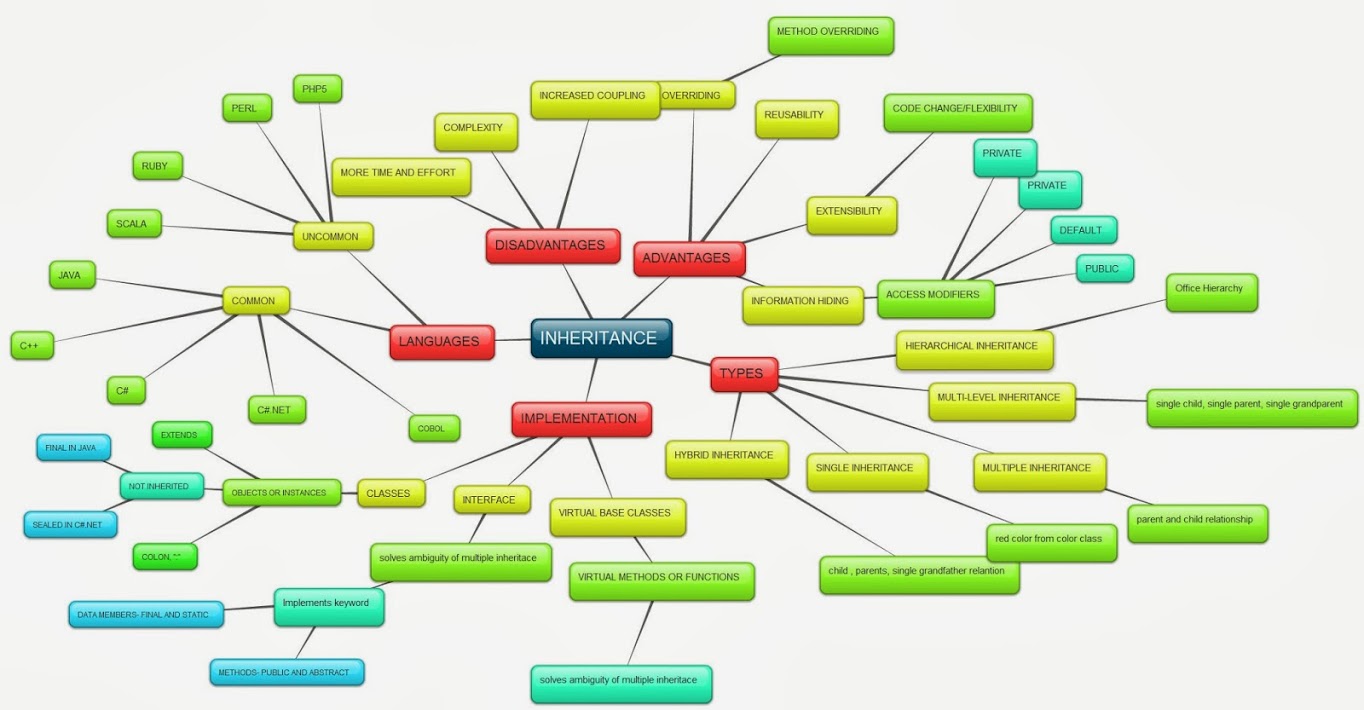
Inheritance
Inheritance is best thought of in simple terms as a system that classifies a hierarchy of types. A cat is a mammal, and a mammal is an animal. If you apply a function to the animal node, it will translate down to the cat node. Applying a function to an amphibian node will affect frogs, but not cats or dogs. If you don't want a cat to have all the attributes applied to the mammal node, it is possible to create an override to counteract the inheritance. However, this creates extra convoluted code and can sometimes lead to programming conflicts that create bugs. Inheritance should not be confused with subtyping.


Emergence
Emergence develops from a few initial rules that have the potential to lead to complex possible outcomes. The loose parameters can cause the program to do things the programmers did not anticipate. Emergence is described as a more organic process that gives the system more control than the programmer, allowing the algorithms to do their thing without much micromanaging or interference.
Emergence is especially interesting to roboticists. Swarm intelligence is when microbots equipped only with simple sensors can work together with a group of microbots in patterns that were not directly built into the programming. Ants and bees kind of do the same thing. The stock market also uses bots to buy and sell shares based on statistical probability, which has lead to some A.I. attempting to outcompete other bots.
When combined with heuristic algorithms, queries, and quantum computing, emergence could lead to self-aware A.I. that learns from experience and adapts accordingly. If the system could self-repair and sustain itself without the intervention of programmers, this would meet the criterion of a living organism.
Aptera Inc.: Emergence in Object-Oriented Programming
TPT.org: Emergence: What Ants can Teach Us

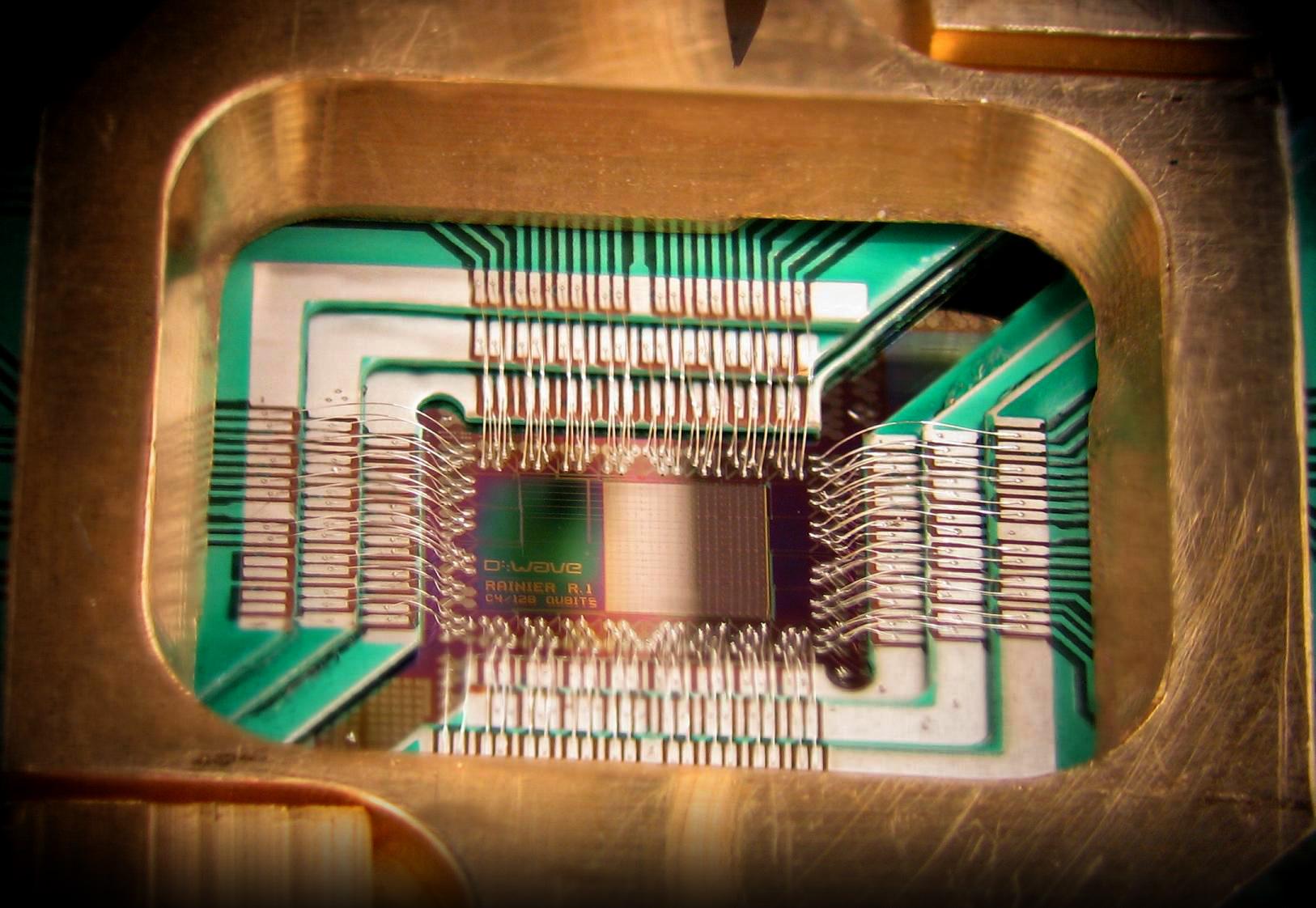
Quantum Computing
Computer science technology is progressing at an incredible rate. It is likely that the next major breakthrough in data storage and transfer will become commercially viable in just a few decades.
The first quantum computer chip has allegedly already been made, and it's stored in what amounts to a $15 million refrigerator. The technical details are a bit daunting for non-physicists, but this technology essentially allows near-instantaneous data transfer over long distances, and can store large amounts of information in a tiny amount of space. There are a ton of implications for how this tech can be used to create highly advanced smart systems.
The Guardian: Has the age of quantum computing arrived?
Forbes: Intel Takes Aim At Nvidia (Again) With New AI Chip And Baidu Partnership

Nanotechnology
Improvements in energy efficiency and materials science advancements drive allow manufacturers to produce smaller and more powerful technology products with each subsequent year. If computers that were once large bulky pieces of hardware can be reduced from the size of a microwave to the size of a portable smartphone, imagine what smart software packed into the size of a molecule could do? The most promising applications for nanotechnology would use microscopic swarms of nanobots programmed to follow simple stimuli. These nanobots could be used for medicinal treatment, smart clothing, regenerating materials, or large scale environmental control like algae.
IBM: A Boy And His Atom: The World's Smallest Movie
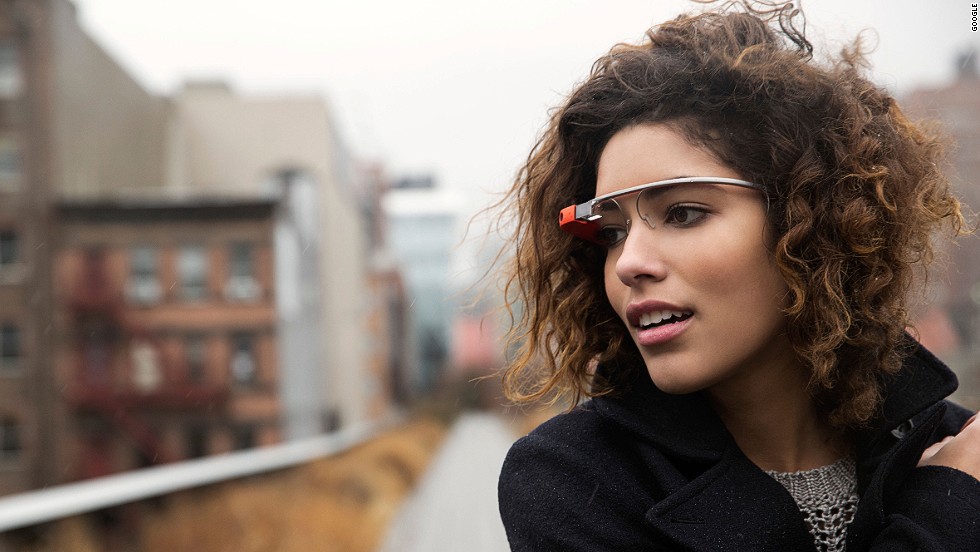


Intelligence Augmentation
Even the most advanced technology still has a lot of inherent limitations when compared to innate human adaptations. Many leading software developers believe that the breakthrough in smart technology lies not in attempting to program complex machines or software that can outperform humans, but in creating tech designed to enhance human abilities. A computer chip implant in the brain could produce an organic supercomputer capable of PHD-level analytics and calculations mixed with human creativity. Wearable computers, power suits, and smart devices could also further extend human abilities far beyond the natural limits. People could interface directly with data, talking with computers to learn and communicate at an inconcievable accelerated rate.
It remains to be seen whether individuals could handle such superhuman powers responsibly. Maybe human augmentation isn't such a great idea from an ethical standpoint, but companies are already capitalizing on products that offer to improve the human condition. The future of smart technology may just be a natural extension of what is already here.
The Conversation: Rise of the humans: intelligence amplification will make us as smart as the machines
io9/Gizmodo: Humans With Amplified Intelligence Could Be More Powerful Than AI
TED Talks: Bill Joy: What I'm worried about, what I'm excited about


Advanced Tutorials- Hopefully Coming Soon
Programming
Datalog
Data Structures
Object-Oriented
Loop
Yield
Global/local variables
Constraints
Float Int
Node
Null Objects
Proxy
Factory Method
Constructor
Builder
Iterator
Refactoring
DRY: Redundancy
Methods and Subroutines
Hierarchies and Chain of Responsibility
Rule of Three
Turing Test, Ebert Test
The Singularity
Pythagorean Theorem
Pascal's Triangle
Triangulation
Dijkstra's Algorithm
Heuristic Algorithms
Finite-State Machine